How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate drone racing. Mastering drone operation requires a blend of technical understanding, safety awareness, and practical skill. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to advanced flight maneuvers and troubleshooting common issues.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will empower you to confidently take to the skies.
We will explore the essential components of a drone, detailing their functions and potential problems. You’ll learn how to plan and execute flights, capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll also delve into crucial safety procedures and regulations, ensuring you fly responsibly and legally. By the end, you’ll possess the knowledge and confidence to operate your drone safely and effectively.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting various drone components and understanding the surrounding airspace. Adherence to safety protocols minimizes risks and ensures a smooth flight experience.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures all drone components are functioning correctly. This reduces the likelihood of malfunctions during flight.
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Visual inspection for cracks, chips, or damage | No visible damage, securely attached | Cracks, chips, loose or bent propellers |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition | Sufficient charge, no swelling or damage | Low charge, swelling, damage |
| GPS | Check GPS signal strength | Strong signal, accurate location | Weak or no signal, inaccurate location |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality | Clear image, proper focus | Blurry image, malfunctioning lens |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check gimbal movement and stability | Smooth and stable movement | Jerky movement, instability |
Understanding Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone requires awareness of local regulations and airspace restrictions. Ignoring these regulations can lead to fines or legal repercussions. Familiarize yourself with your local laws and the airspace around you.
Common airspace restrictions include areas near airports, stadiums, and other sensitive locations. Many countries have designated no-fly zones that are strictly enforced. Utilizing drone mapping apps can help visualize restricted areas.
Emergency Procedures

Having a plan for emergencies is paramount. Knowing how to react to malfunctions or signal loss can prevent accidents and protect your drone.
- Malfunction: Attempt to return to home (RTH) if possible. If RTH fails, try to guide the drone to a safe landing area.
- Signal Loss: If signal is lost, the drone should ideally have a return-to-home (RTH) function that will automatically bring it back. If not, you may need to rely on visual contact and manually maneuver it back if you can still see it.
Safe Operating Practices
Safe operating practices minimize the risk of collisions and accidents. Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone, and avoid flying near people or obstacles.
- Maintain visual line of sight at all times.
- Avoid flying near people or animals.
- Be aware of surrounding obstacles, including trees, buildings, and power lines.
- Fly at a safe altitude, respecting any local regulations.
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation system is fundamental to safe and efficient operation. This section will cover calibrating your drone, understanding control functions, and mastering various flight modes.
Drone Compass and GPS Calibration
Proper calibration of the compass and GPS is crucial for accurate flight. Incorrect calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior.
- Power on the drone and ensure it has a strong GPS signal.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for compass calibration. This usually involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern.
- Once the compass is calibrated, the drone will typically indicate successful calibration through visual or audible cues.
- Ensure the GPS has acquired sufficient satellites for accurate positioning before taking off.
Drone Remote Control Functions
A typical drone remote has several controls, each with a specific function. Understanding these functions allows for precise drone manipulation.
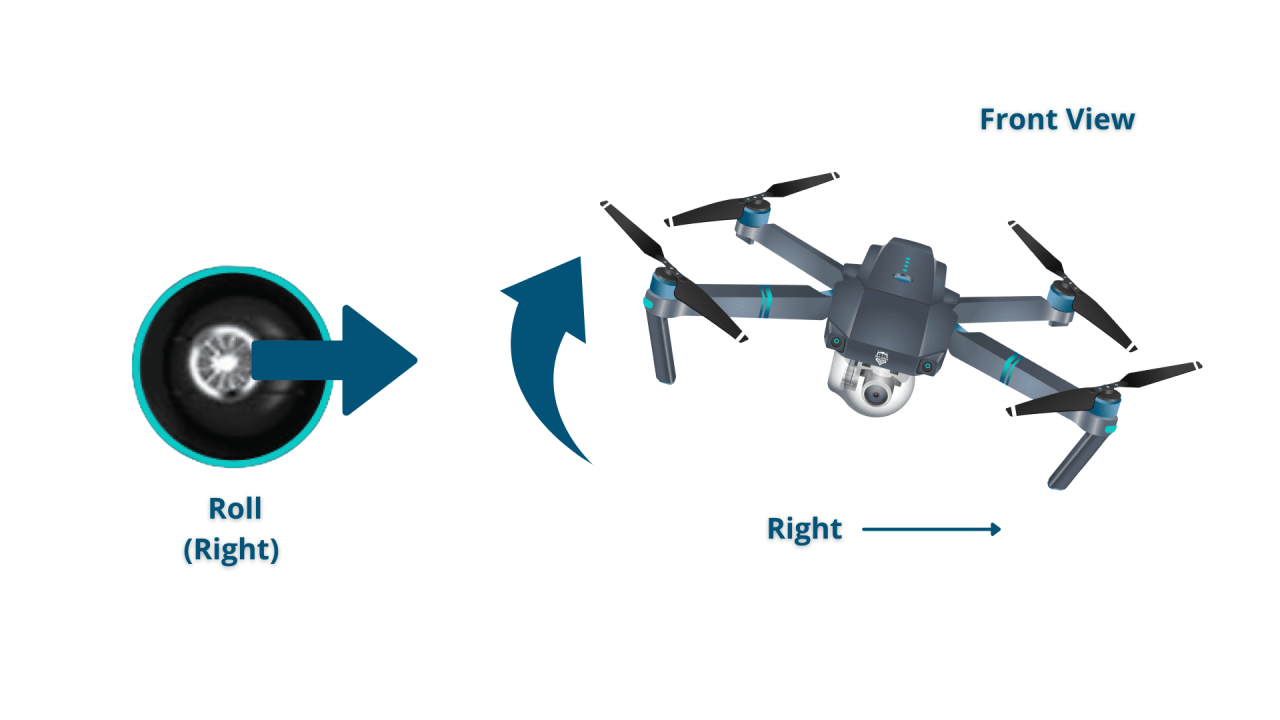
- Left Stick: Controls the drone’s yaw (rotation) and throttle (vertical movement).
- Right Stick: Controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement).
- Return to Home (RTH) Button: Initiates the automated return of the drone to its home point.
- Emergency Stop Button: Cuts power to the motors, causing an immediate descent.
- Camera Controls: Buttons to adjust camera settings like zoom, photo/video recording.
Flight Modes
Most drones offer different flight modes to suit various skill levels and flight situations. Understanding these modes is key to safe and efficient operation.
- Beginner Mode: Limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, ideal for beginners.
- Sport Mode: Increases the drone’s speed and responsiveness, allowing for more dynamic maneuvers (requires more skill).
- GPS Mode: Uses GPS for position holding and return-to-home functionality.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation regardless of GPS signal.
Smooth Drone Maneuvers
Practicing smooth maneuvers is essential for precise flight and stunning aerial footage. This includes mastering take-off, landing, and hovering techniques.
- Take-off: Gradually increase throttle until the drone lifts off smoothly.
- Landing: Slowly decrease throttle until the drone gently touches down.
- Hovering: Maintain a steady throttle to keep the drone at a fixed altitude and position.
Flight Planning and Mission Execution
Effective flight planning ensures safe and efficient mission execution, resulting in high-quality aerial footage. This involves designing flight paths, programming waypoints, and optimizing camera settings.
Sample Flight Plan for Aerial Photography
A simple flight plan might involve capturing images of a landscape from various angles. This example assumes the use of waypoint navigation.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of the regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation hinges on thorough preparation and practice.
- Take-off Point: Designated safe area, clear of obstacles.
- Waypoint 1: Altitude 50 meters, capturing a wide shot of the landscape.
- Waypoint 2: Altitude 30 meters, capturing a closer shot of a specific feature.
- Waypoint 3: Altitude 20 meters, capturing a detail shot.
- Return to Home (RTH): Drone automatically returns to the take-off point.
Programming a Drone Flight Path
Many drones and accompanying apps allow for pre-programming flight paths. This ensures consistent and repeatable shots.
- Open the flight planning software.
- Set the home point.
- Add waypoints, specifying altitude, speed, and camera settings for each point.
- Review the planned path to ensure accuracy and safety.
- Upload the flight plan to the drone.
Drone Camera Settings
Understanding camera settings allows for optimal image quality. Different settings impact the final image in various ways.
| Setting | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | Controls depth of field, allowing for creative blurring of backgrounds | Wider apertures let in more light, potentially causing overexposure in bright conditions |
| Shutter Speed | Controls motion blur, allowing for freezing action or creating motion trails | Faster shutter speeds require more light, potentially leading to underexposure in low light conditions |
| ISO | Controls image sensitivity to light, useful in low-light conditions | Higher ISO values can introduce noise (grain) into the image |
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
High-quality aerial photos and videos require consideration of lighting and composition. Golden hour (sunrise and sunset) often provides the most flattering light.
- Lighting: Shoot during golden hour for soft, warm light. Avoid harsh midday sun.
- Composition: Utilize the rule of thirds for visually appealing shots. Consider leading lines and framing to enhance the image.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance extend the lifespan of your drone and ensure its continued safe operation. This involves storage, cleaning, and firmware updates.
Drone Storage and Battery Care
After each flight, the drone and its battery require careful handling and storage. This protects the components from damage and ensures battery longevity.
- Power down the drone completely.
- Carefully store the drone in a safe, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Store the battery separately, in a designated storage case, away from flammable materials.
- Allow the battery to cool before storing.
Drone Cleaning and Inspection
Regular cleaning and inspection identify potential damage early on. This prevents small issues from becoming larger problems.
- Use a soft cloth to gently wipe away dirt and debris from the drone’s body and propellers.
- Inspect the propellers for cracks, chips, or damage.
- Check all connections and components for any signs of wear or damage.
Firmware and Software Updates
Keeping your drone’s firmware and software up-to-date is crucial for optimal performance and safety. Updates often include bug fixes and new features.
- Check the manufacturer’s website for the latest firmware and software updates.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for updating the firmware and software.
- Ensure the drone is fully charged before starting the update process.
Extending Battery Lifespan
Proper battery care significantly extends its lifespan and ensures optimal performance. Avoid extreme temperatures and overcharging.
- Avoid fully discharging the battery.
- Avoid overcharging the battery.
- Store the battery in a cool, dry place.
- Use the manufacturer’s recommended charger.
Understanding Drone Components and Their Functions: How To Operate A Drone
Familiarity with the various components of a drone and their functions is essential for effective operation, troubleshooting, and maintenance. This includes propellers, cameras, and the flight controller.
Key Drone Components
A drone consists of several interconnected components, each playing a crucial role in its operation.
| Component | Function | Importance | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flight Controller | Controls the drone’s flight, including stability and responsiveness | Essential for stable and controlled flight | Malfunction, software glitches |
| Motors | Provide power to the propellers | Essential for propulsion | Motor burnout, malfunction |
| Propellers | Generate thrust for flight | Essential for flight | Damage, imbalance |
| Battery | Provides power to the drone | Essential for flight duration | Low charge, damage, swelling |
| GPS Module | Provides location and navigation data | Essential for precise flight and RTH | Weak signal, malfunction |
| Camera | Captures images and videos | Essential for aerial photography and videography | Malfunction, image quality issues |
Drone Propeller Types
Different types of propellers impact flight performance. Choosing the right propeller is essential for optimal flight characteristics.
- Standard Propellers: Offer a balance of speed and stability.
- Low-Noise Propellers: Reduce noise levels but may slightly reduce performance.
- High-Performance Propellers: Offer increased speed and agility but may be noisier.
Drone Camera Systems

Various drone camera systems cater to different needs and budgets. Choosing the right camera depends on the intended application.
- High-Resolution Cameras: Offer detailed images and videos but are often more expensive.
- Wide-Angle Cameras: Capture a broader field of view, ideal for landscape photography.
- Zoom Cameras: Allow for closer shots without physically moving the drone.
Drone Selection for Specific Tasks
Selecting the right drone for a specific task is crucial for achieving optimal results. Consider factors like payload capacity, flight time, and camera capabilities.
- Aerial Photography: A drone with a high-resolution camera and stable gimbal.
- Inspections: A drone with a long flight time and zoom capability.
- Mapping: A drone with advanced mapping features and GPS accuracy.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding how to troubleshoot common drone issues can save time and prevent potential damage. This section covers solutions to various problems, from battery warnings to crashes.
Solutions to Common Drone Problems, How to operate a drone
Several common issues can arise during drone operation. Knowing how to address these problems is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency.
- Low Battery Warning: Land the drone immediately and recharge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an open area with a clear view of the sky, ensuring sufficient satellite signals.
- Propeller Malfunction: Inspect the propellers for damage. Replace any damaged propellers.
- Drone Crash: Carefully inspect the drone for damage. Repair or replace any damaged parts.
- Motor Failure: This may require professional repair or replacement of the affected motor.
Interpreting Error Messages
Error messages displayed on the drone’s remote or app provide valuable information for troubleshooting. Consult the manufacturer’s documentation to understand the meaning of each error message.
Common error messages may include low battery, GPS signal loss, or motor issues. The specific error message will guide you toward the appropriate solution.
Recovering a Crashed or Stuck Drone
Recovering a crashed or stuck drone requires careful attention to safety and the environment. Assess the situation before attempting recovery.
- Ensure the area is safe before approaching the drone.
- Carefully remove any obstructions preventing the drone from being retrieved.
- Inspect the drone for damage before attempting to fly it again.
Contacting Customer Support
If you encounter persistent issues or are unable to resolve a problem, contacting the manufacturer’s customer support is recommended. They can provide expert assistance and guidance.
Provide detailed information about the issue, including error messages, flight conditions, and any troubleshooting steps already taken.
Operating a drone successfully combines technical knowledge with responsible piloting. From understanding pre-flight safety procedures to mastering flight controls and post-flight maintenance, each step contributes to a safe and enjoyable flying experience. By adhering to regulations, practicing safe flight techniques, and regularly maintaining your equipment, you can unlock the full potential of your drone and capture incredible aerial perspectives.
Remember, responsible drone operation ensures both your safety and the safety of those around you, allowing you to explore the exciting world of aerial technology with confidence and skill.
FAQ Corner
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functionality.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to help you get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will help you safely and effectively navigate the skies with your drone, ensuring a positive experience from beginning to end.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’re in a new location or near magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Flight time varies depending on the drone model and battery size. Check your drone’s specifications for an estimate.
What is the best way to clean my drone?
Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe down the drone body. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
